
 |
| 1.3.1 |
| TOOLS OF THE OCEANOGRAPHER: Equipment: Sampling Tools |
| A. Taking Samples of the Marine Environment | |
| 1. Water Samplers • Van Dorn Bottle • Nansen Bottle • Niskin Bottle • JZ Bacterialogical Bottle • Surface Sample Bottle | 2. Messengers Most of the water samplers can be sent to a particular depth and then "triggered" to take the water sample by a "messenger". This is also the case with several other types of samplers (bottom, organism). |
| 3. Bottom Samplers • Ekman Grab • Petersen Grab • Soft Bottom Modified Petersen Grab • Wash Bucket • Bottom Corer | 4. Animal and Plant Samplers • Plankton: Standard Plankton Net, Deck Plankton Collector, Folsom Plankton Splitter, Sedgewick-Rafter Plankton Counting Chamber • Succession Plates • Transects • Quadrants • Biological Dredge • Beach Seine • Otter Trawl • Isaacs-Kidd Midwater Trawl |
| Ruler used in most images for scale | |||||||
|
| 1. Water Samplers |
| Van Dorn Bottle | |||||||
 |
|
| Nansen Bottle | |||||||
 |
|
| Niskin Bottle | |||||||
 |
|
| JZ Bacterialogical Bottle | |||||||
 |
|
| Surface Sample Bottle | |||||||
 |
|
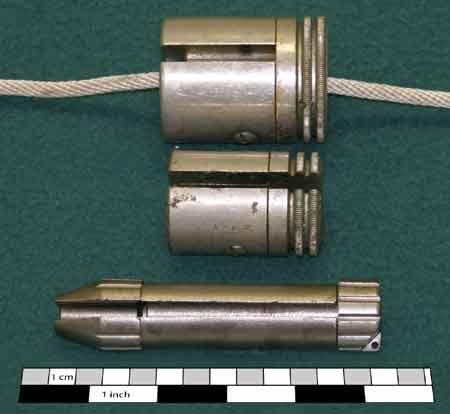
| 2. Messengers |
| Messengers | |||||||
 |
| ||||||
| 3. Bottom Samplers |
| Ekman Grab | |||||||
 |
|
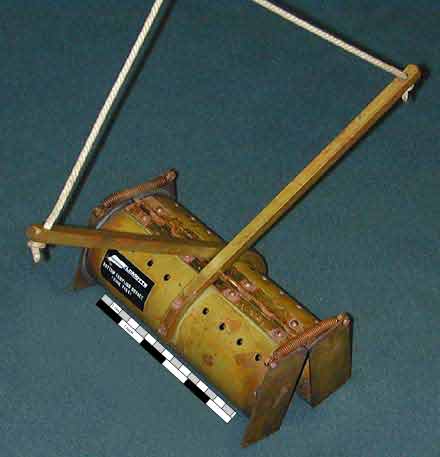
| Petersen Grab | |||||||
 |
|
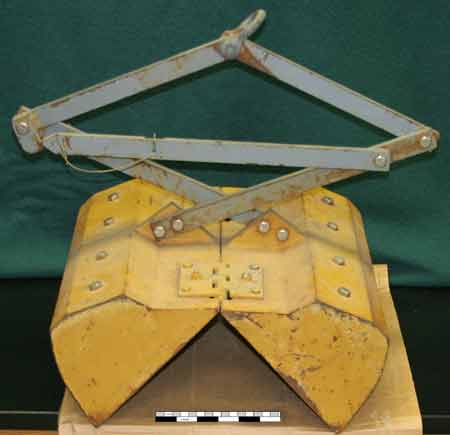
| Soft Bottom Modified Petersen Grab | |||||||
 |
|
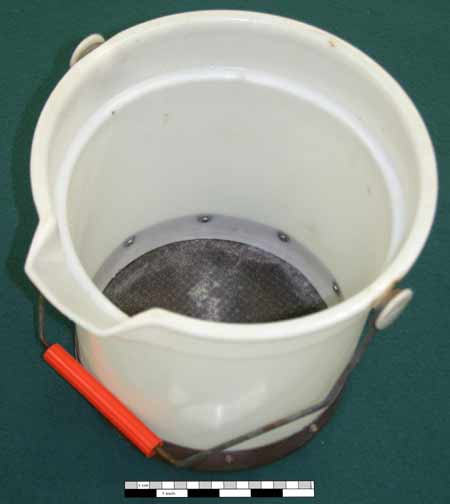
| Wash Bucket | |||||||
 |
|
| Bottom Corer | |||||||
 |
|
| 4. Animal and Plant Samplers |
| Standard Plankton Net | |||||||
 |
| ||||||
| Deck Plankton Collector | |||||||
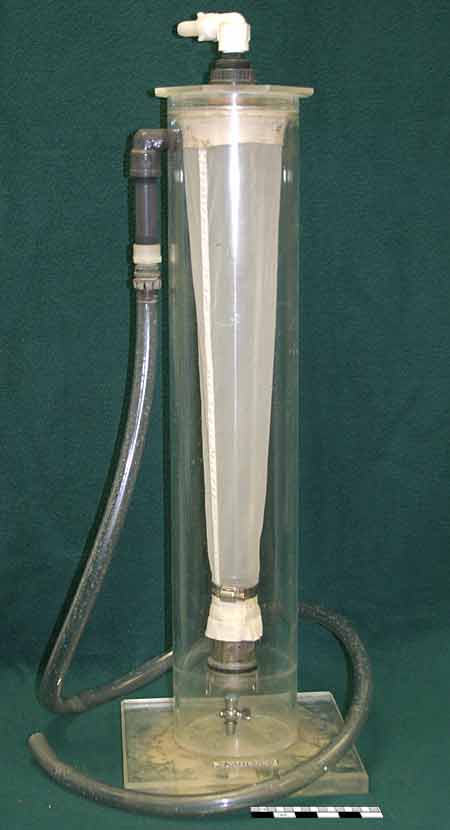 |
|
| Folsom Plankton Splitter | |||||||
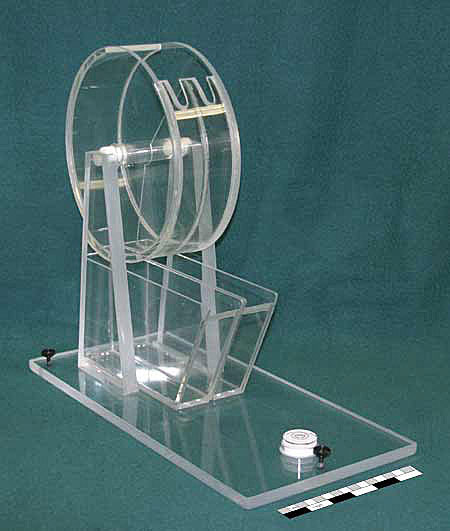 |
|
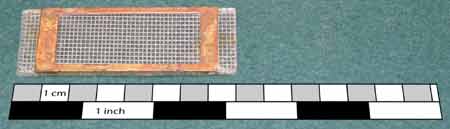
| Sedgewick-Rafter Plankton Counting Chamber | |||||||
 |
|
| Succession Plates | |||||||
 |
|
| Transects | |||||||
  |
|
| Quadrats | |||||||
 |
|
| Biological Dredge | |||||||
 |
|
| Beach Seine | |||||||
 pulling the beach seine  viewing the beach seine catch |
|
| Otter Trawl | |||||||
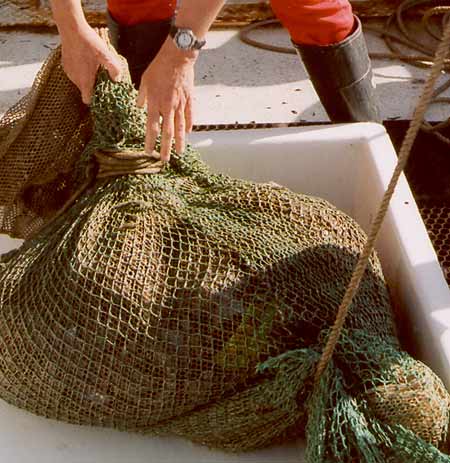 End of otter trawl 70' net.  Otter trawl catch |
|
| Isaacs-Kidd Midwater Trawl | |||||||
 |
|
(Revised 8 July 2004) |